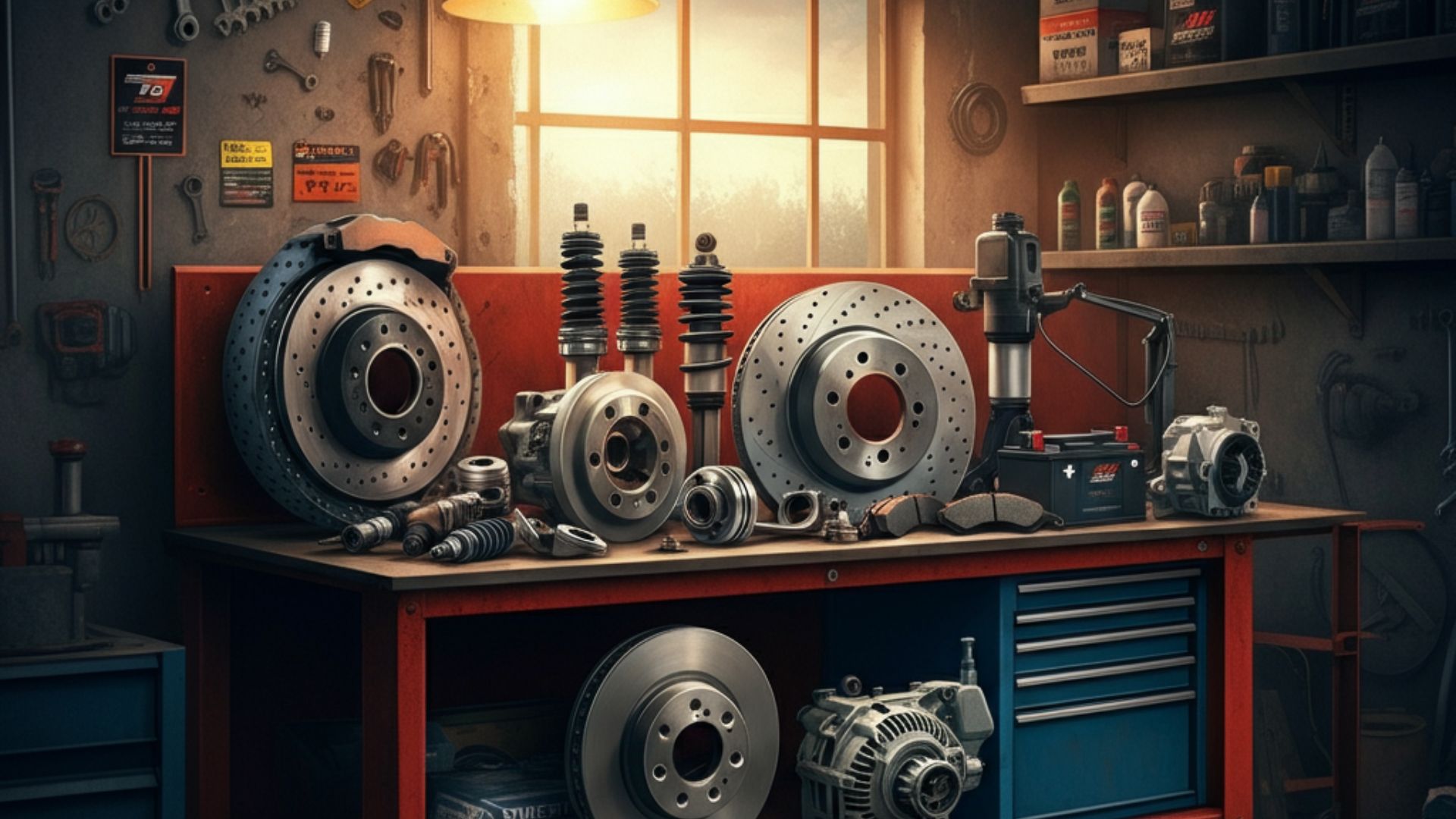
Cars are complex machines made up of thousands of parts working in harmony. Whether you’re a car owner looking to save on repair costs or an enthusiast eager to understand more, knowing the essential components of your car is empowering. This guide breaks down the major car systems, explores key components, provides maintenance tips, and helps you troubleshoot common issues. You’ll be more confident diagnosing and managing your vehicle’s needs by the end.
Getting to Know Your Car Parts
Before we look at specific systems, it’s essential to understand why familiarizing yourself with car parts matters. Knowledge of your car’s anatomy can help you:
- You can save money by learning how to perform basic maintenance tasks yourself, such as changing oil, replacing air filters, and checking tire pressure.
- Understanding key terms and knowing how to describe issues clearly can help you communicate effectively with mechanics, avoiding unnecessary repairs.
- Proper care, including regular servicing, cleaning, and following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, will enhance your vehicle’s longevity.
- Troubleshoot minor issues quickly and confidently, such as identifying warning lights, fixing minor leaks, or replacing worn-out wiper blades before they become more significant problems.
Read on to discover the vital systems and components within your car.
1. Engine Components
Think of the engine as your car’s heart. It burns fuel to produce power, and within it are critical components that keep the vehicle running smoothly.
Key Parts of the Engine
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine’s cylinders. Without them, your car won’t start.
- Pistons: Inside the cylinders, pistons compress the fuel-air mixture to generate energy.
- Timing Belt or Timing Chain: Ensures the sync between the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft so valves open and close at the right time.
- Oil Filter and Oil Pump: Help clean and lubricate the engine’s moving parts to reduce wear.
- Radiator: This plays a critical role in cooling the engine by dissipating heat from the coolant, preventing the engine from overheating.
- Fuel Pump: Moves the fuel from the gas tank to the engine, ensuring it’s delivered at the correct pressure for optimal performance.
- Alternator: This generates electrical power to charge the battery and run electrical systems when the engine runs.
- Air Filter: Keeps debris, dirt, and other particles from entering the engine, ensuring clean air is mixed with the fuel.
- Starter Motor: Provides the initial power needed to turn the engine over and start combustion.
- Spark Plugs: Ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders, creating the explosions that power the engine.
- Battery: Supplies electrical energy to start the engine and powers various electrical components when the engine is not running.
- Exhaust System: Directs and controls the vehicle’s emissions and reduces engine noise, promoting a cleaner and quieter operation.
- Timing Belt: Synchronizes the movement of the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring valves open and close appropriately during each cylinder’s intake and exhaust strokes.
Maintenance Tips for Your Engine
- Replace spark plugs every 30,000-100,000 miles, depending on your car model and driving conditions. Worn spark plugs can reduce fuel efficiency and cause engine misfires, so staying on top of this maintenance is crucial for optimal performance.
- Change your oil and filter every 5,000–7,500 miles, or as specified by your owner’s manual, to keep your engine running smoothly and prevent sludge buildup. Regular oil changes help extend your engine’s lifespan and improve overall driving performance.
- Inspect the timing belt or chain regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or missing teeth, and replace it as your car manufacturer recommends (typically every 60,000-100,000 miles). A failing timing belt can cause significant engine damage, so proactive replacement is essential to avoid costly repairs.
Troubleshooting the Engine
- Problem: Difficult starts or no start.
- Check: Ensure the battery is fully charged and the connections are secure. Inspect the spark plugs for wear or damage and replace them if necessary. Verify fuel levels to ensure enough fuel in the tank, and check the starter motor to confirm it is functioning correctly.
- Problem: Engine misfires.
- Check: Examine the spark plugs for signs of wear, corrosion, or improper gaps and replace them if needed. Clean or replace dirty fuel injectors to ensure proper fuel delivery to the engine.
- Problem: Overheating.
- Check: Check coolant levels to ensure the system is filled correctly and look for leaks in the coolant system. Inspect the radiator for clogs or damage, and make sure the cooling fans function. Also, test the thermostat to see if it is stuck or broken and replace it if necessary.
2. Braking System
The braking system ensures your ability to slow down or stop safely. Its components work together to convert kinetic energy into heat energy.
Key Parts of the Braking System
- Brake Pads: Friction material that presses against the rotors to slow your car.
- Rotors or Brake Discs: Metal discs connected to the wheels, where brake pads create friction.
- Brake Calipers: House the brake pads and push them against the rotors when you press the brake pedal.
Maintenance Tips for Your Brakes
- Inspect brake pads every 12,000 miles and replace them before they wear too thin (typically around 3mm thickness). Worn brake pads can reduce stopping power and stress other brake components unnecessarily.
- Check brake fluid levels regularly, as low fluid can impact braking efficiency. Replace the brake fluid every two years to maintain optimal performance and prevent contamination, which can lead to system failure over time.
- Look for signs of warped rotors, such as a pulsing brake pedal, squealing noises, or vibrations when braking. Warped rotors can affect braking smoothness and should be resurfaced or replaced to ensure safe driving.
Troubleshooting Brakes
- Problem: Squealing noise when braking.
- Check: This could be caused by worn-out brake pads that need replacement or a lack of lubricant on the contact points between the brake pad and caliper. Over time, the pad friction material wears down, resulting in metal-on-metal contact that produces this noise. Regular maintenance can help prevent this.
- Problem: Spongy brake pedal feel.
- Check: A spongy or soft brake pedal indicates air trapped in the brake lines or low brake fluid levels. Air in the brake system interferes with the hydraulic pressure needed for effective braking. Bleed the brakes and check for any fluid leaks causing the low levels.
- Problem: The car pulls to one side while braking.
- Check: If your vehicle pulls to one side during braking, it might be due to uneven brake pad wear or a stuck caliper on one side of the vehicle. A stuck caliper prevents proper pressure distribution, causing the vehicle to veer. Inspect and service the brake pads and calipers to restore balance and safety.
3. Suspension System
The suspension system keeps your ride smooth and your car stable over uneven terrain.
Key Parts of the Suspension System
- Struts and Shocks (Shock Absorbers): Control the spring movement to ensure a smooth ride.
- Coil Springs or Leaf Springs: These absorb impact during bumps and aid in supporting the vehicle’s weight.
- Control Arms and Bushings: Connect the suspension to your car frame, allowing controlled movement.
Maintenance Tips for Your Suspension
- Check shocks and struts for leaks, cracks, or other visible damage every 50,000 miles, or more frequently if you frequently drive on rough terrain or uneven roads. Worn shocks can affect your vehicle’s handling and safety, so replacing them on time is essential.
- Ensure tires are correctly aligned and balanced to reduce uneven wear on your tires and suspension components. Misaligned tires can cause your vehicle to pull to one side and lead to costly repairs if not addressed.
- When driving over bumps or uneven surfaces, pay attention to unusual noises, like clunking, creaking, or knocking sounds. These noises can indicate worn or damaged suspension parts that need immediate attention.
Troubleshooting Suspension
- Problem: Uneven tire wear.
- Check: Inspect the wheel alignment, as improper alignment can cause tires to wear down unevenly over time. Additionally, check the condition of the springs or shocks, as worn suspension components can also lead to uneven contact with the road, accelerating tire wear.
- Problem: The car bounces excessively after a bump.
- Check: This is often a sign of worn shocks or struts responsible for stabilizing your car after hitting bumps. Inspect these components for leaks, cracks, or other signs of wear, as they may need to be replaced to restore smooth driving.
- Problem: The Vehicle leans to one side.
- Check: A broken spring or a damaged control arm can cause the car to sit unevenly, leading to a noticeable lean. Thoroughly inspect the suspension system to identify any compromised parts, as these will need to be repaired or replaced to ensure proper balance and handling.
4. Electrical System
Your car’s electrical system powers everything from starting the engine to playing your favorite tunes.
Key Parts of the Electrical System
- Battery: Provides the initial power to start the engine.
- Alternator: Recharges the battery while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Turns over the engine to get it running.
Maintenance Tips for Your Electrical System
- Clean battery terminals regularly to prevent corrosion, as buildup can interfere with the battery’s connection and reduce efficiency. Use a mixture of baking soda and water or a specialized terminal cleaner for best results.
- Test your battery every six months, especially during extreme hot or cold weather, as these conditions can strain its performance. A simple battery test ensures it’s holding a proper charge and avoids unexpected breakdowns.
- Replace the alternator belt according to your car’s service schedule, as a worn or faulty belt can affect the alternator’s ability to charge the battery. Regular inspection can help catch wear and tear early.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
- Problem: The car doesn’t start, but the lights work.
- Check: This could indicate an issue with the starter motor or ignition switch. The starter motor may not be engaging to turn the engine over, or the ignition switch could be faulty and fail to send power to the starter. Have these components been inspected and tested?
- Problem: Dim headlights or flickering interior lights.
- Check: This is often a sign of an issue with the alternator or voltage regulator. The alternator might not be generating enough power to keep the electrical system fully operational, or the voltage regulator could be struggling to maintain a steady flow of electricity. Both should be checked and repaired if needed.
- Problem: Dead battery.
- Check: If your battery keeps dying, it may be due to a parasitic drain (something in the car is drawing power even when it’s off) or a faulty alternator that isn’t recharging the battery correctly. Test for a drain and ensure the alternator functions correctly to avoid recurring battery issues.
Keep Your Car in Top Shape
Knowing your car parts and systems makes maintaining your vehicle less daunting, whether you’re a DIY mechanic or just want to stay informed.
General Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspections: Dedicate 5-10 minutes each week to visually inspect your car for any wear and tear, such as tire damage, fluid leaks, or unusual noises. Catching these minor issues early can prevent more significant problems down the road.
- Preventative Maintenance: Always follow your manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, brake checks, and filter replacements. Staying proactive can help you avoid costly repairs and keep your car running smoothly for longer.
- Use Quality Parts and Fluids: Choose genuine or high-quality aftermarket options when replacing parts or topping off fluids. These ensure better reliability, improved performance, and a longer lifespan for your vehicle. Using subpar products may save money upfront but could lead to expensive issues later.
Get Familiar with Your Car
Every car has its unique quirks. Spend time with your owner’s manual, which contains valuable maintenance schedules and troubleshooting tips.
Take the Driver’s Seat in Car Care
Understanding your car’s key components ensures safety, saves money, and may ignite a passion for vehicles. That’s why knowing your car parts is a must for every driver. Start by focusing on one system, and build your knowledge piece by piece.
Want to take your car expertise a step further? Subscribe to our newsletter for more DIY tips and advice. You’ll also receive updates on the latest car parts and accessories to help you customize and maintain your vehicle. In addition, following automobile blogs or participating in online forums can also expand your knowledge about your car’s specific make and model.
Keep Your Car Running Smoothly
Regular maintenance checks are vital to keep your car running smoothly. These include essential visual inspections, tire pressure checks, oil changes, and fluid top-ups. By performing these simple tasks yourself, you can save money on costly repairs in the long run.
You should also pay attention to any warning signs from your car, such as unusual noises or dashboard lights turning on. Ignoring these warnings could lead to further damage, which can be expensive.
FAQs
Q.1 What is the recommended frequency for oil changes?
Ans. Changing your oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles is generally recommended, but consult your car’s manual for the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Q.2 How often should I check my tire pressure?
Ans. Check your tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips.
Q.3 What should I do when the check engine light comes on?
Ans. When the check engine light comes on, it’s best to have your car checked by a mechanic as soon as possible to avoid potential issues.
Q.4 How often should I replace my air filter?
Ans. Air filters should generally be replaced every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or as your car manufacturer recommends.
Q.5 When should I rotate my tires?
Ans. Rotating your tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles is advised to promote even wear.
Q.6 What fluids should I regularly check in my car?
Ans. Regularly check your engine oil, coolant, transmission fluid, brake fluid, and windshield washer fluid.
Q.7 How can I improve my car’s fuel efficiency?
Ans. Maintain proper tire pressure, avoid aggressive driving, and ensure regular maintenance to fuel your car.
Q.8 How often should I inspect my brakes?
Ans. Brakes should be inspected at least once a year or if you notice any unusual sounds or reduced braking performance.
Q.9 How do I know if my battery needs to be replaced?
Ans. Signs like a slow engine start, dim lights, or a bloated battery case indicate it may need replacement.
Q.10 Should I warm up my car before driving in cold weather?
Ans. Modern cars do not require long warm-ups; 30 seconds is sufficient before driving.
Q.11 When should I replace my windshield wipers?
Ans. Replace windshield wipers every 6 to 12 months or when you notice streaks and reduced visibility.
Q.12 Can I top off my fluids by myself?
Ans. You can top off fluids like windshield washer fluid, but consult your manual for the correct procedures and types of fluids.
Q.13 How can I tell if my tires are worn out?
Ans. Look for tread wear indicators or use the penny test to check for sufficient tread depth.
Q.14 What causes strange noises from my car?
Ans. Strange noises could indicate issues with the brakes, suspension, or the engine that require a mechanic’s attention.
Q.15 Is following the scheduled maintenance in my car’s manual necessary?
Ans. Following the maintenance schedule ensures your car operates efficiently and prevents costly repairs.
You may read this: How to Maintain Your Car When it’s Not in Use












1 thought on “Know Your Car Parts: A Guide for DIY Mechanics and Enthusiasts”